Have you recently begun trading options? This guide will help you understand and implement a simple options strategy. Perfect for newbies, we’ll break down basic option strategies, letting you select the option trading strategy for beginners that you prefer. Get ready to learn about beginner options strategies in a clear, easy-to-follow way.
Key takeaways
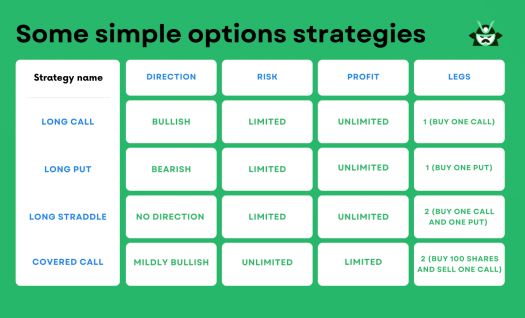
- A simple options strategy is generally identified in long puts and long calls. They are considered low-risk strategies because of their limited downside potential.
- Long straddles represent a slightly less simple options strategy combining buying a call and a put. It’s simple because it has limited risk and no need to guess the direction of the stock.
- The Covered call is a simple options strategy involving selling a call option while holding an equivalent amount of the underlying asset. It has many of the characteristics of holding a stock position, so it’s often the ‘gateway’ strategy for options trading.
Simple Options Strategies
A simple options strategy revolves around contracts that give you, the investor, the right to buy or sell an asset at a pre-determined price before a set expiration date. These strategies are not only easy to implement option strategies, but they’re also ideal as an option trading strategy for beginners.
Options can be a versatile part of your investment strategy. They offer the potential for profit in almost any market condition and allow for managing risk and enhancing income.
Beginner options strategies often include the long call and long put strategies. A long call is when you believe the price of an asset will rise, so you buy a call option to profit from that expected increase. A long put, on the other hand, is used when you expect the asset’s price to fall.
Other common strategies include the long straddle, betting on significant price movement in either direction, and the covered call, where you own the underlying asset and sell call options to earn premium income. Here is a table that compares each simple options strategy mentioned in today’s article:
Long Call
A long call is a simple options strategy where you purchase a call option, betting on an increase in the underlying asset’s price. It’s considered a basic option strategy and is often recommended as an option trading strategy for beginners.
Think of it this way: opening a long call is like buying 100 shares for a limited time (depending on the expiration date of your option).
The reason why a long call is seen as a low risk options strategy is because your potential loss is limited to the premium you paid when buying the option. The underlying asset’s price could drop to zero, but your loss wouldn’t exceed your initial investment. This makes it an appealing beginner options strategy.
Implementing a long call simple options strategy is straightforward. First, identify an asset you believe will increase in price. Then, buy a call option for that asset with a strike price – the price at which you can buy the asset – close to its current market price.
If the asset’s price increases above the strike price before the option’s expiration date, you can exercise the option to buy the asset at the strike price and then sell it at the higher market price for a profit. If the price doesn’t rise as expected, you can let the option expire worthless, limiting your loss to the premium paid.
Long Call Example
Suppose you’re bullish on Citigroup (C) stocks, currently trading at $54.33. With an upcoming earnings announcement, it becomes a stock to watch closely. Utilizing an options screener like Option Samurai, you notice an unusually high trading volume on the $57 call contract. This is part of your simple options strategy. As you see below, the options screener can give you the type of option you need to buy (a call), the quantity (one contract), the expiration date, the strike price, and the other option-related details you may want to consider.
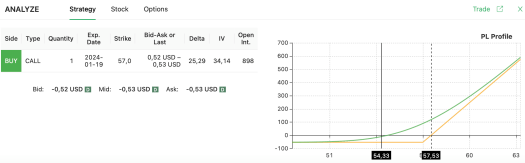
Consider that, in the case pictured above, your maximum loss would be the premium you paid for the option. Instead, the profits would increase in a linear way once you pass the breakeven price (i.e., C needs to close above $57.53 by the time the option expires).
However, taking advantage of short-term price jumps around earnings announcements is a common basic option strategy. So, if the stock price increases after the earnings are announced, you could consider closing the trade early for a profit.
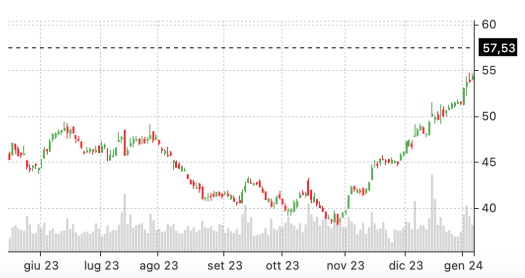
While this might seem like an attractive option trading strategy for beginners, it’s crucial to tread with caution. Earnings outcomes can be unpredictable, and the stock has been on a bullish run for several months already.
Also, implied volatility (IV), which often inflates option prices before earnings, typically drops sharply after the announcement (a phenomenon we all know as IV Crush). This could make the trade less profitable than it initially appears, emphasizing the need for careful analysis in beginner options strategies.
Note that the low risk does not simply come from the strategy you choose, but also from the underlying asset. For instance, given the long-term bullish market trend, a long call SPY options strategy with expiration in 6 months may be a relatively safe move.
Long Put
After seeing the long call, it’s fairly easy to understand the long put, a simple options strategy that involves buying a put option. In contrast to a long call, with a long put you’re betting on the price of the underlying asset decreasing.
In simple terms, you can think of the long put strategy like selling 100 stocks for a limited amount of time (once again, the temporal limit is given by the expiration date of the put).
Similar to the long call, the long put is considered a basic option strategy and an excellent option trading strategy for beginners due to its limited risk. The most you can lose is the premium you paid for the put option, making it a low-risk approach even if the asset’s price skyrockets.
To implement a long put strategy, you first need to identify an asset you believe will decrease in price. Next, buy a put option for that asset with a strike price close to its current market price. If the asset’s price falls below the strike price before the option’s expiration date, you can exercise the option, selling the asset at the higher strike price.
If the asset’s price doesn’t fall as expected, you can let the option expire, limiting your loss to the premium paid. This beginner options strategy allows you to profit from a downward market movement with controlled risk.
Long Put Example
Let’s examine Nio (NIO), a stock known for its high volatility. Using Option Samurai, you might find there’s been substantial trading volume around the $7 put option, even though NIO is currently priced at $8.06. This gap may appear large, but with a high-beta stock like NIO, and an option far from expiration, such fluctuations aren’t unusual.
In the picture below, you see how the options screener highlights the possibility of buying the $7 put we mentioned. Keep an eye on the graph on the right, as it portrays the P&L profile of the strategy (you can only lose the option premium in the worst-case scenario, and your profits grow linearly on the left-hand side of the chart).
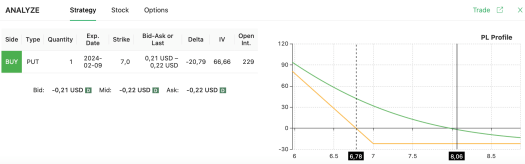
To profit from this simple options strategy, NIO needs to drop below $6.78 by the time the option expires. Given NIO’s volatility, it could be worthwhile to close your position early if a decent profit emerges. Remember, basic option strategies often involve managing risk and taking profits when they appear.
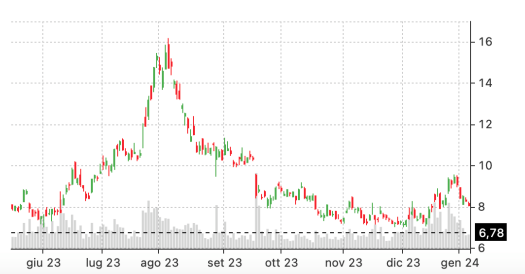
In this scenario, with no earnings event between the trade’s opening and the option’s expiration, the chances of an IV crush are lower. This makes it a suitable option trading strategy for beginners, who should always consider the likelihood of significant price swings in their beginner options strategies.
Long Straddle
If you understood how the long call and long put strategies work, you’ll have no trouble grasping the long straddle, another simple options strategy. A long straddle involves buying both a call option and a put option for the same underlying asset, with the same strike price and expiration date.
With a long straddle, you can think of yourself as simultaneously buying long and selling short 100 shares for a limited amount of time.
Like other basic option strategies, the long straddle is considered low-risk because the most you can lose is the total premium paid for the two options. This makes it an ideal option trading strategy for beginners who wish to speculate on significant price movement in either direction but want to limit potential losses.
Implementing a long straddle strategy is straightforward. First, identify an asset you believe will have a major price move but are uncertain in which direction it will go. Then, simultaneously buy a call option and a put option with the same strike price close to the current market price and the same expiration date.
If the price swings significantly in either direction, one of your options will become profitable while the other will expire worthless, potentially netting a profit. This beginner options strategy allows investors to profit from volatility, regardless of the direction the market moves.
Long Straddle Example
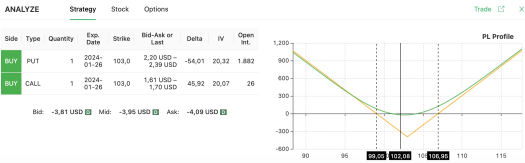
Let’s delve into Nike (NKE), currently priced at $102.08. Suppose you anticipate significant price movement, even without an earnings event, perhaps due to potential announcements from NKE’s competitors. This forms part of your simple options strategy.
In this situation, you could establish a simple options strategy with long straddle position on NKE by purchasing both a put and a call at the $103 strike price. To make a profit, NKE would need to move either above $106.95 or below $99.05 by the option’s expiration date. This is one of the basic option strategies that doesn’t bank on a specific direction but rather on a sizeable price move in either direction.
Note in the picture below how your maximum loss will be limited to the option premiums in the unlikely case that the stock price is exactly $103 on the expiration date. Instead, your profits will grow in a linear manner, both on the upside and downside scenarios.
It’s always wise to examine the stock’s price chart. In this case, you might notice that each time NKE has entered the $99.05 – $106.95 range, it quickly moved out of it.
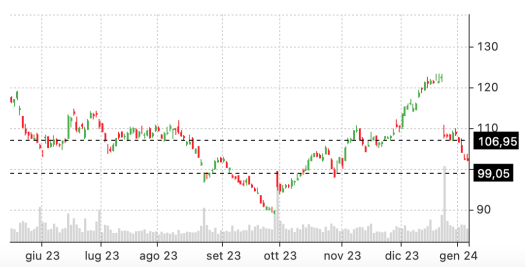
This pattern may lead you to believe that the long straddle could be an appealing trade. As with all beginner options strategies, it’s crucial to understand the dynamics of the stock and the market before implementing any option trading strategy for beginners.
Covered Call
Finally, the covered call is another commonly used simple options strategy. It involves owning or buying shares of the underlying asset and selling a call option on those shares.
This strategy is pretty much like buying and holding a stock while also renting it. If you think of it this way, you’re simply looking at a modified version of a buy-and-hold trade.
This strategy is considered a basic option strategy and an ideal option trading strategy for beginners due to its risk management potential. The risk associated with a covered call is lower because you own the underlying shares. This means that even if the option is exercised and you’re required to sell the shares, you already own them and don’t need to buy at potentially unfavorable market prices.
Implementing a covered call strategy involves two steps. First, you either buy shares or use shares you already own of an asset you believe will slightly increase or remain flat in price. Then, you sell a call option on these shares with a strike price above the current market price.
If the price stays below the strike price, the option expires worthless and you keep the premium from selling it, effectively reducing your overall cost basis. If the price rises above the strike, you’ll have to sell the shares at the strike price but you’ll still profit from the premium and the increased value of the shares.
This is one of the beginner options strategies that not only generates income but also provides a cushion against small price drops. Note that this strategy will not protect you if the stock price decline is significant.
Covered Call Example
Let’s explore a covered call strategy using Apple (AAPL), which is currently trading at $181.18. If you’re bullish on AAPL, you might opt to buy 100 shares and sell a $185 call option as part of your simple options strategy. This approach hedges your risk by generating income through the sold call option.
Note that, as pictured below, your maximum loss (the left-hand side of the chart) is uncapped, while this strategy limits the amount of profit you can earn.
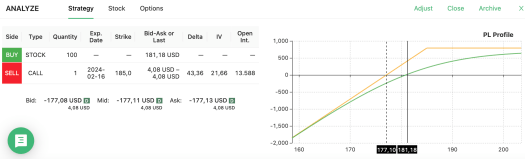
Here’s how it works: if AAPL’s price doesn’t drop below $177.10, you’ll still make a profit when the option expires. This provides a buffer against minor price declines, making it a viable basic option strategy.
However, there’s a trade-off. If AAPL’s price significantly increases, your profits are capped at the strike price of the sold call option. You won’t benefit from any increase beyond the $185 mark.
This is a common option trading strategy for beginners because it reduces risk and generates income, but it also limits potential gains. As with all beginner options strategies, it’s key to understand both the benefits and drawbacks before diving in.
Clearly, after looking at all these examples, it’s clear that you should privilege a simple options strategy such as a long call or long put whenever you’re fairly sure about the market direction. However, if you’re more uncertain about where the market is headed, implementing a long straddle strategy could be the way to go. Lastly, the covered call is a good simple options strategy if you’re quite bullish on a stock but fear that there may be minor price declines.

