One of the many advantages of trading options is the ability to design a low volatility option strategy. If you’re looking for the best option strategy for low volatility, you will have a relatively large choice. This approach leverages low IV options strategies to increase potential returns even in less volatile markets.
Key takeaways
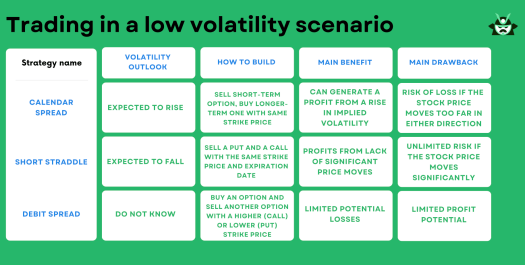
- The Calendar Call Spread, Short Straddle, and Put and Call debit spreads are effective strategies for profiting from low-volatility situations.
- Technical indicators like ADX can be used to spot periods of limited volatility, making it easier to implement these strategies successfully.
- A low-volatility option strategy will require the stock to move in a range for as long as you choose to keep the trade open.
Best Option Strategy for Low Volatility
A low volatility option strategy can be a game-changer for anyone. It’s a method that allows traders to profit even when market fluctuations are minimal.
To understand this, let’s first clarify what low volatility in the market means. Essentially, it refers to a situation where price changes are small and infrequent. In such scenarios, many traders might feel stuck, but with the right option strategy for low volatility, you can still make gains.
The key lies in understanding and implementing low IV options strategies. These strategies focus on options with low implied volatility (IV), which are typically less expensive and thus offer a higher potential return on investment. Intriguing, isn’t it?
Now, you might be wondering, what is the best option strategy for low volatility? To help you better understand this, we’ll look into three strategies: Calendar Call Spread, Short Straddle, and Put and Call debit spreads. The table below summarizes the aspects we’ll look into:
The Calendar Call Spread Strategy
The Calendar Call Spread is a compelling low volatility option strategy. This approach is used when you anticipate the stock price to remain neutral or drop slightly in the short-term. The real gain comes from a price increase after the short-term contract expires but before the longer-dated one closes. This method has a maximum loss defined by the trade’s entry cost.
In a perfect scenario, the stock price is at or just below the short call at expiration, allowing the short contract to expire worthless. Then, you’ll need to decide whether to exit the long call position or wait for potential increases in the stock price or implied volatility.
So, how do you create a Calendar Call Spread? It involves selling-to-open a short-term call option and buying-to-open a later-expiring call option, both at the same strike price. This low volatility option strategy requires paying a debit at entry, which is also the maximum risk if the short call option ends up in-the-money.
In short, you will pick this strategy once you expect implied volatility to rise up to a certain point. The trade limits the losses into which you may incur, with a potential profit that, in absolute terms, is generally much higher than the potential loss.
Example of Calendar Call Spread Strategy
Let’s illustrate a low volatility option strategy with a practical example. Imagine we’re trading Caterpillar (CAT), known for its low historical volatility. With CAT’s current price at $297.37, we could initiate a Calendar Call Spread strategy on the $295 strike price.
Using an options screener like Option Samurai, we can get a clear picture of the potential profit and loss profile of this low volatility option strategy before diving in. Simply put, for this strategy to work, we need the stock price to be above $285.82 and below $305 by the time the two options expire.
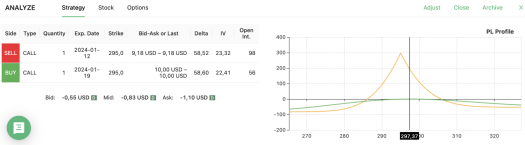
However, it’s important to remember that we may not keep this position open until expiration. We might choose to close one of the two legs earlier based on market trends or our investment goals. This flexibility is part of what makes the Calendar Call Spread a best option strategy for low volatility.
The Short Straddle Strategy
The Short Straddle is another low volatility option strategy. Here, you sell both a call and put option with identical strike prices and expiration dates. This strategy comes into play when you predict that the underlying asset won’t move much higher or lower during the options contracts’ lifespan and that volatility is not expected to increase.
The maximum profit from this method equals the premium collected from writing the options. However, potential loss can be unlimited, so it’s typically used by advanced traders.
Short straddles allow traders to profit from a lack of movement in the underlying asset, rather than banking on significant price shifts. The aim is to let both the put and call expire worthless, collecting premiums when the trade opens.
But there’s a risk for assignment as the chances of the asset closing exactly at the strike price at expiration are low. Still, if the price difference between the asset and strike price is less than the collected premiums, you’ll turn a profit.
Advanced traders often use this low volatility option strategy to capitalize on a potential drop in IV. If implied volatility is unusually high with no clear reason, the call and put may be overpriced.
The goal then would be to wait for volatility to decrease, then close the position for a profit without waiting for expiration. It’s an effective option strategy for low volatility situations. If you expect volatility to fall and do not fear a potentially uncapped loss, this may be the right strategy for you.
Example of Short Straddle Strategy
Let’s consider an example of a Short Straddle strategy using IBM, expecting it to go through a low volatility phase. With IBM’s price at $161.22, we’d want the stock to stay between $155 and $165 by expiration to make this low volatility option strategy work.
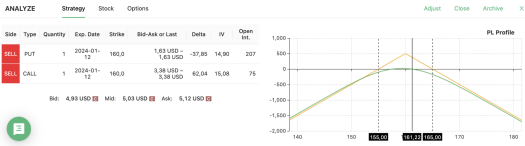
However, even with a low beta stock like IBM, it can be challenging to pinpoint a prolonged period of low volatility. This uncertainty often leads traders to close the position well before it expires, especially if they’ve recorded a profit along the way.
This move aligns with the nature of a Short Straddle strategy which is not about predicting significant price moves, but profiting from the lack of them. It’s a low volatility option strategy that requires patience and a keen eye on market trends. But when executed correctly, it can be one of the best option strategies for low volatility scenarios.
Put and Call Debit Spreads
Put and Call Debit Spreads are another type of low volatility option strategy. In a Put Debit Spread, also known as a bear put spread, you purchase a put option and simultaneously sell another put option at a lower strike price. Both options have the same expiration date.
The goal here is to profit from a moderate decline in the price of the underlying asset. Your maximum profit is the difference between the two strike prices, minus the net cost of the options. This low volatility option strategy is used in low-volatility situations because it profits from a lack of significant price movement in the underlying asset.
Similarly, a Call Debit Spread involves buying a call option and selling another call option with a higher strike price. It’s used when expecting a moderate rise in the price of the underlying asset.
Both these strategies offer a way to reduce upfront costs, limit potential losses and profit from low-volatility scenarios, making them a viable choice for the best option strategy for low volatility.
Note that, while with the previous strategies you generally need to have a clear volatility outlook, debit spreads work differently. In this case, you may simply find yourself in a situation in which you do not know whether volatility will go up or down. There’s no shame in that, as the market itself won’t send clear signals in several situations, and it’s good to know that there’s a strategy that covers this scenario.
Example of Put and Call Debit Spread Strategy
Let’s imagine you’re expecting a period of low volatility and have a slightly bearish outlook on EOG. The stock currently trades at $123.40, and you decide to open a bear put spread strategy. This low volatility option strategy allows you to profit from a moderate decrease in the price of the underlying asset.
In this scenario, your maximum profit would be reached if EOG stays below $125. To break even or make a small profit, the stock would need to be below $129.20.
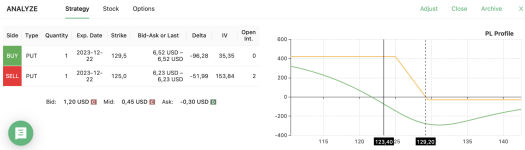
Given the relatively low loss above $129.20, you might be tempted to wait until the options expire. However, a more risk-averse approach would be to sell for a profit before expiration if the stock price declines after you open the position. This tactic illustrates how put and call debit spreads can serve as an effective low iv options strategy when handled with patience and a clear understanding of market trends.
Spotting Periods of Limited Volatility
Finding periods of limited volatility is crucial in implementing a low volatility option strategy. The Average Directional Index (ADX) can be an effective tool for this. Low ADX values, typically below 25, suggest weak trends and thus periods of low volatility (instead, for a high volatility option strategy, you may choose to look at when the indicator moves above 25).
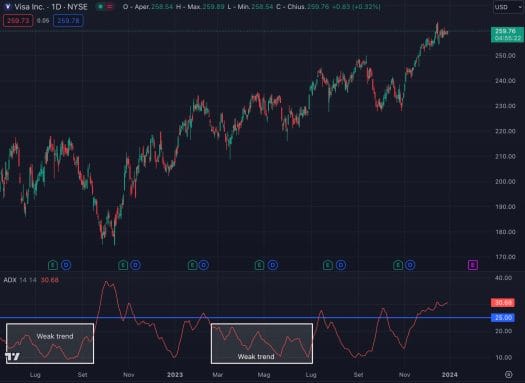
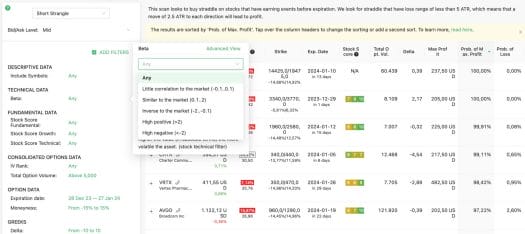
Your choice of stock also matters. High beta stocks, being more volatile, require a wider profit range to accommodate larger price swings. On the other hand, low beta stocks are less volatile, and a narrower profit range could suffice as significant price changes are less likely. You could use Option Samurai’s beta filter to spot, for instance, look for a good short straddle opportunity by playing around with the beta value, as shown below:
In addition to ADX, Option Samurai users may also employ the Real Volatility (RV) percentile filter and explore the implied volatility suite. This filter allows traders to assess the stock’s real volatility in comparison to historical data. For instance, an RV percentile below 50 indicates volatility below the median, while a reading below 20 signifies that it’s among the 20% lowest volatility levels in the last year.
Adding the Option Samurai RV filter helps traders analyze volatility better, giving extra insight into potential trades. Using these techniques makes it easier to spot low-volatility times. This skill makes it simpler to use low implied volatility (IV) options strategies and pick the right option strategy for the current low volatility situation.

